Parasites in the human bodyappear completely unexpectedly. The reason for this usually becomes direct contact with the source of the infection, for example, with an infected person or object. There are many types of parasites that can settle in the human body: they can be lamblia, earthworms, alveococci, Trichinella, schistosomes, etc.
Parasites in the human body

The human body has a rather complex structure, which is susceptible to various diseases and infections, infections, viruses and parasites. Parasites that inhabit the human body are microorganisms that lead a parasitic lifestyle, trying to survive by feeding on other organisms, microorganisms, cells, and so on.
Parasites that live in the human body are microorganisms that lead a parasitic lifestyle, trying to survive by feeding on other organisms, microorganisms, cells, etc.
Parasites that find fertile ground for life and reproduction in the human body, cause very serious, sometimes irreparable damage to its health, destroy the body from the inside, eat it, and sometimes lead to death or stop the work of certain organs, which also impairs quality of lifeperson, depresses and eventually shortens his life.
There are millions of species of parasitic worms in nature. Of these, there are those that parasitize on only one representative of the animal world. But in nature there are also species that can exist in the body of several species of animals. Many people ask which parasites live in the human body.
A huge species of helminths can live in the human body. Some of them are very rare, while others very often settle inside and can lead a parasitic lifestyle for up to several decades.
Types of parasitism
There are the following types of parasitism: ectoparasitism - parasites that lead a superficial lifestyle on the human body. This category includes lice, bugs, ticks; endoparasitism - parasites that affect a person's internal organs. They, in turn, are divided into two large groups of protozoa and helminths.
Species of parasitic protozoa: lamblia, toxoplasma, trichoionada. These types of protozoan parasites are most commonly found in the human body.
The classification of parasites associated with helminths implies their division into three major groups: nematodes; trematode; cestode.
Types of parasites in the human body
Pinworms
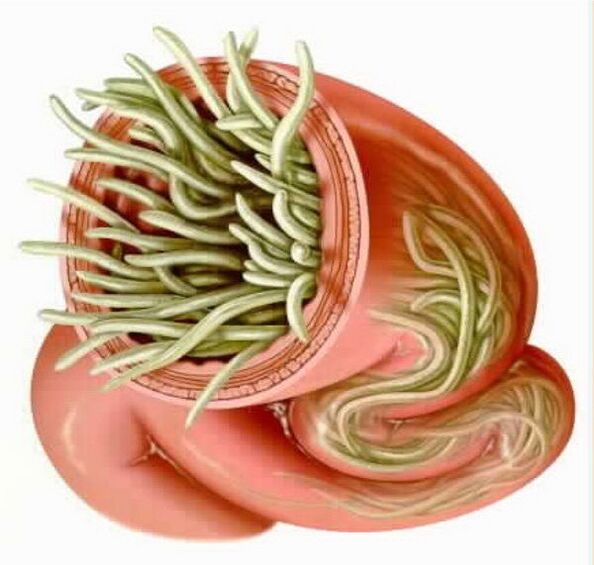
Pinworms are the most famous parasites in the gut. The disease caused by pinworms is called enterobiasis. Not only humans are sick, but also great apes. Children are at increased risk of pinworm infection. According to various sources, the level of their involvement in enterobiasis in preschool age ranges from 25 to 90%. Pinworms are transmitted from one person to another. Infection occurs by handling, clothing, and any objects touched by the sick person, provided that after contact the hands are not washed and pinworm eggs enter the mouth (this is especially common during meals).
Flies and cockroaches can lay the eggs of these nematode worms by sowing food. Pinworms live in the small intestine, in the appendix, in the large intestine. They mate in the ileum, after which the female crawls out of the anus through the rectum and lays eggs in the anus.
Symptoms of enterobiase are itching in the anal area, intoxication of the body (allergic reactions, exhaustion, fatigue), anemia, increased levels of eosinophils in the blood, insomnia and abdominal pain.
To get rid of enterobiases, anthelmintic drugs are used. The dosage and method of treatment are chosen by the doctor. To avoid re-infection, it is important to keep your hands clean, wash them after visiting any public place, after using the toilet, before eating, etc.
Nails should be cut short, the bed and underwear thoroughly disinfected, and the apartment cleaned daily.
Toxocara
Toxocara is a parasite from the nematode group. The disease caused by toxocariasis is called "toxocariasis". This invasion of humans can be larval (ocular and visceral) as well as intestinal. The disease is spread all over the world. Toxocara infection occurs when worm eggs enter the human digestive tract. This is most often seen when eating food or water contaminated with dog feces. Contact with sick animals is no less dangerous.
The natural carriers of Toxocare are cats and dogs, foxes and wolves. Once in the human body, the worm larva migrates through blood vessels and can settle in any organ. The symptoms of the disease will depend on it. Toxocariasis most often manifests itself in the form of allergic reactions (Quincke's edema, skin rash, bronchial asthma). During the worsening of the disease, the body temperature can rise up to 38 degrees, but the symptoms of body intoxication are weak.
Enlarged lymph nodes may suspect toxocariasis: the most common is a visceral form of toxocariasis, occurring with damage to internal organs (intestines, respiratory system, heart valves).
A person may experience abdominal pain, right hypochondria, dyspeptic disorders, nausea; if the respiratory system is damaged, the person has difficulty breathing, dry cough, choking attacks; if toxocara are deposited on the heart valves, then the patient has weakness, blue fingers and nasolabial triangle, difficulty breathing; the shape of the skin is characterized by itching, a feeling of movement under the skin, inflammation of the skin and mucous membranes; in its neurological form the parasite causes the development of inflammation of the meninges and the brain tissues themselves.
Manifested by headaches, nausea and vomiting, seizures and other neurological disorders. Anthelmintic drugs as well as pathogenetic and symptomatic therapy are used to treat toxocariasis.
Human Ascaris
Human Ascaris is a roundworm that parasitizes on the small intestine. The disease that these parasites cause is called ascariasis. The owner of the roundworm and the source of infection is a sick person. Together with their feces, the worm eggs enter the soil, where they mature to larvae. Then this soil is transferred to food or into human hands, and if the rules of personal hygiene are not respected and if fruits, vegetables and berries are poorly processed, it is transferred to the digestive tract.
Children and residents of rural areas are more susceptible to infections. Ascariasis manifests itself in different ways at different stages of its development. In the phase of larval migration through the body, there is an increase in body temperature, a dry cough occurs, wheezing in the lungs, and lymph nodes increase in size. Children suffer more from ascariasis than adults.
Allergic skin reactions are a characteristic symptom of ascariasis. During intestinal parasitism, the patient develops dyspeptic disorders, loose stools are replaced by constipation, frequent abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting occur. Hysterical attacks, insomnia, mental fatigue and headaches are noticed in the part of the nervous system.
To treat ascariasis in the larval migration phase, patients are prescribed some anthelmintic drugs while others parasitize on intestinal worms.
Hookworm and some
Hookworm and some are two species of roundworms that belong to the Ancylostomatidae family and cause a disease called hookworm. There are two ways of infecting the human body with these parasites - fecal-oral (drinking contaminated water, fruits, vegetables) and percutaneous in contact with the ground (penetration occurs through the skin).
Clinical symptoms of hookworm: papular vesicular rash, shortness of breath and cough, loss of appetite, nausea, abdominal pain, loose stools, iron deficiency anemia. Treatment is reduced to taking anthelmintic drugs and eliminating anemia with iron preparations.
Wide ribbon
Broad tapeworm refers to tapeworms of the order Pseudophyilidea. These parasites live in the small intestine of humans and fish-eating mammals. Tapeworm infection provokes the development of diseases such as diphyllobotriasis.
There are 12 types of tapeworms that can parasitize the human body, however, the widest tapeworm is the most common. Infection occurs when eating raw and thermally unprocessed lightly salted fish or caviar containing worm eggs. Symptoms of the presence of parasites in the intestines: nausea, abdominal pain, anemia.
In severe cases, intestinal obstruction develops. To get rid of the parasite, patients are prescribed antiparasitic drugs. After completing the therapeutic course, another study is required due to the presence of worms in the body. If necessary, the use of anthelmintic drugs is repeated.
Bull tapeworm
The bull tapeworm is a tapeworm belonging to the teniid family. In the larval stage it affects cattle, and in the tapeworm stage it lives in the human body (in the intestines). Tapeworm causes a disease called teniarinhosis, as a rule, one parasite is present in the patient's body. Human infection occurs through food after eating poorly cooked meat (beef).
Clinically, the disease is manifested by nausea, excessive appetite, abdominal pain, unstable stools and allergic reactions such as urticaria. An anthelmintic is prescribed to remove bovine tapeworm from the body. In parallel, the patient should adhere to a diet without slag, put cleansing enemas, take laxatives. After using an anthelmintic, the worm dies and leaves the human body naturally. Sometimes its length can be up to 12m.
Pork tapeworm
Swine tapeworm is a parasitic tapeworm that infects mammals. Medium carriers can be pigs, dogs, rabbits, camels, but the ultimate owner is always man.
If an adult parasite is found in the human body, they are talking about such a disease as teniasis. When the parasite is in the patient's body in the larval stage, the disease is called "cysticercosis".
Pork tapeworm infection occurs when pork that has not been cooked is eaten. Sometimes sources of cysticercin sow hands or water. A patient with teniasis presents an epidemiological danger both for himself (infections with the larvae of the brain, skin, eyes or skeletal muscles), and for others.
Symptoms of tenia: abdominal pain, loss of appetite, upset stools, headache, frequent dizziness, fainting (brain and eye tenia is extremely dangerous). To treat tenia, the patient is hospitalized. Under the supervision of a doctor, he was prescribed anthelmintic drugs, after which after 2 hours the patient takes a physiologically soluble laxative, which allows him to get rid of segments and eggs of worms. Surgery is needed to treat cysticercosis of the eyes and brain.
Ehinokok
Echinococcus is a tapeworm of the order Cyclophyllidae. Adults parasitize in the intestines of dogs and cats, and are found in jackals and wolves. For humans, the larvae of the parasite are dangerous, which can cause a serious disease - echinococcosis. The larvae can infect a person's internal organs, creating echinococcal cysts in them. For echinococci, humans act as an intermediate host.
Infection is carried out by contact (in the process of cutting carcasses, in interaction with a sick animal) or food (when eating contaminated food or water). At risk are people who are engaged in animal husbandry or who have constant contact with animals. Symptoms may not appear for many years.
When the asymptomatic stage is over, pain, itchy skin and urticaria appear at the site of larval invasion. In addition, the work of the organ within which the larva of echinococcus parasitizes suffers. Rise in body temperature and fever are observed during cyst suppuration.
A complete cure for echinococcosis is possible only by surgery. The cyst is peeled off, taking care not to damage its membrane. If the bladder is very large, then it is punctured and the contents are sucked out. Before and after surgery, the patient is prescribed antiparasitic drugs. In the case of radical cyst removal, the prognosis for recovery is favorable.
Alveokoki
Alveococcus is a helminth from the cestode group. The worm cries out for a life-threatening disease of alveococcosis, characterized by the formation of a primary focus in the liver with subsequent spread of metastases to other organs. Infection occurs when parasite oncospheres enter the mouth.
This can happen during hunting, in the process of cutting the corpses of wild animals, in contact with domestic animals or when you eat unprocessed berries and herbs from the forest. Symptoms of alveococcosis are reduced to pain in the right hypochondrium, belching, nausea. There is often itching, allergic reactions. Suppuration of the tumor by the parasite and its penetration into the abdominal or pleural cavity is not excluded.
Alveococcal metastases can be found in the brain and lungs. Treatment of the disease is rapid, but it should be supplemented by the intake of antiparasitic drugs.
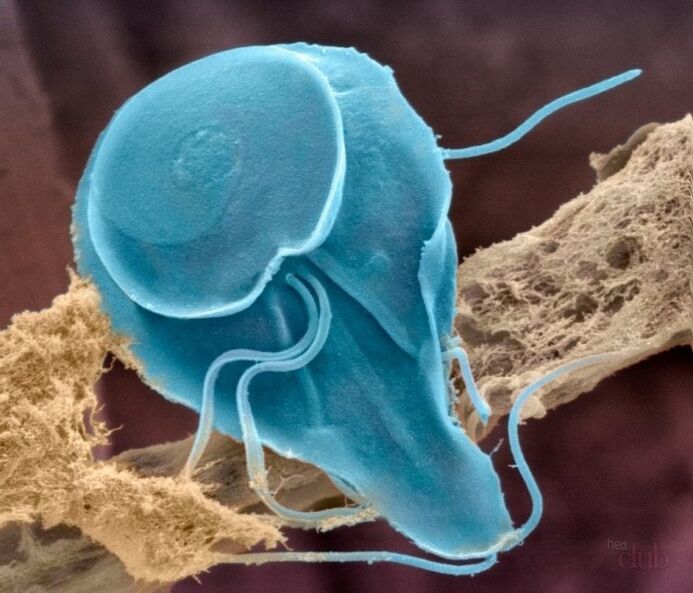
Giardia
Giardia (another name for Giardia) are whipworms that belong to the order Diplomonadid. Giardia causes a disease called “giardiasis” and parasitizes the small intestine in humans as well as in many other mammals and even birds.
Giardia infection occurs through the fecal-oral route: food, water and household contact methods. In terms of transmitting the infection, the use of raw water, contaminated food, and the use of public objects sown with lamblia cysts are of the greatest importance. The leading symptoms of giardiasis are nausea, abdominal pain, stool disorders, and excessive gas.
In addition, patients suffer from allergic reactions, intoxication and neurotic disorders. Giardiasis therapy is performed with the help of antiprotozoal drugs, as well as with the inclusion of enzymes, choleretic agents and enterosorbents in the treatment regimen.
Histological amoeba
Histologically an amoeba is a protozoan parasite that causes a disease called amoebiasis. The disease is manifested by the formation of ulcers on the colon, followed by damage to other internal organs. Amoeba infection occurs by the fecal-oral route, after mature cysts from water or food enter the human gastrointestinal tract. Possible contact transmission of parasites through unwashed hands. Flies can be carriers of amoebae.
Another way of spreading amoebiasis is through sexual intercourse (anal intercourse). Symptoms of amoebiasis: profuse mucous stools, abdominal pain, blood in the stool, weight loss, anemia. In addition, extraintestinal amoebiasis is characterized by the formation of abscesses in those organs that are affected by parasites (lungs, brain, liver, etc. ).
Antiprotozoal drugs are prescribed to treat intestinal ambiasis.
The duration of therapy is determined by the severity of amoebiasis.
A disease called gnathostomosis is caused by the larvae and sexually mature nematodes of Gnathostoma spinigerum. Infection occurs when eating unprocessed fish, frog meat or poultry, as well as when drinking uncooked, uncontaminated water. Symptoms of the disease are manifested in cough and pain at the site of penetration of the larva under the skin, in local inflammation and increase in body temperature.
Severe edema and itching are typical. As a rule, after a week from the onset of symptoms, they disappear, but recur over the years. Dangerous damage to the eyeball and brain is often fatal. Treatment includes taking anthelmintic drugs and surgery. During surgery, parasites are removed under the skin.
Trichinella
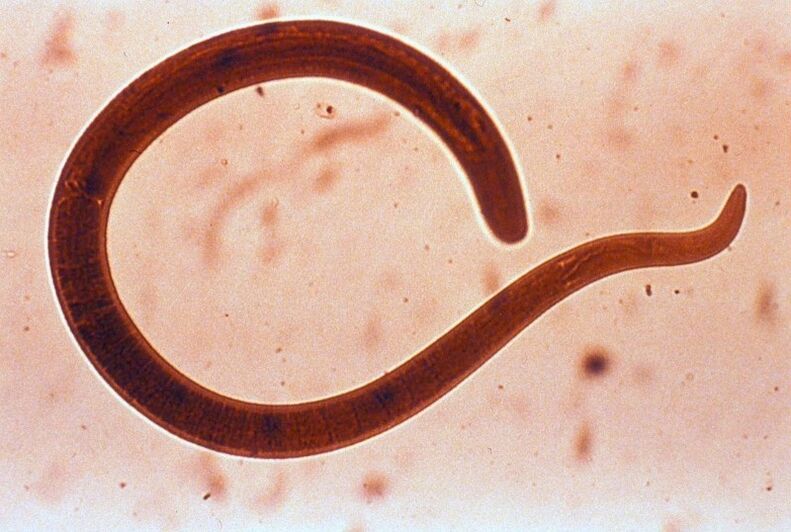
Trichinella are round parasitic worms that in the larval stage live in the muscles (oculomotor, masticatory, diaphragm muscles), and in adulthood - in the lumen of the small intestine. The disease caused by Trichinella is called "Trichinellosis". It's deadly.
Infection in humans occurs through the consumption of raw or poorly processed meat from wild and domestic animals. Symptoms include loss of appetite, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. In the future, it will be accompanied by muscle pain, swelling of the eyelids and a rash on the skin. Treatment of parasitic infection is carried out with the help of anthelmintic drugs. At the same time, antihistamines and, if necessary, corticosteroids are prescribed.
Schistosomes
Schistosomes are fluke worms of the genus trematodes. They cause a disease called schistosomiasis. Human infection occurs during bathing, in the process of washing clothes or flooding the ground with water with schistosome larvae. They are able to penetrate the human body even through intact skin and mucous membranes. Symptoms in the acute phase of the disease are manifested in a rise in temperature to a high level, in itchy skin and in the appearance of papules all over the body.
They are able to penetrate the human body even through intact skin and mucous membranes. Symptoms in the acute phase of the disease are manifested in a rise in temperature to a high level, in itchy skin and in the appearance of papules all over the body.
After the disease becomes chronic, the infected person may show signs of colpitis, prostatitis, colitis, ascites, hydronephrosis, etc. Anthelmintic drugs are used to treat the disease. Surgical intervention is required for complications of genitourinary schistosomiasis.
There are many parasites that can harm the human body. Most of them enter the body of their owner through the gastrointestinal tract if the technology of safe food preparation is not followed and basic hygiene procedures are not followed.
Parasites in the body - adaptive properties
- long life expectancy (helminths live in the human body for years, and sometimes while the host parasite lives);
- ability to suppress or modify the immune response of the host organism (immunodeficiency occurs, conditions are created for the penetration of pathogenic agents from the outside, as well as for "disinhibition" of internal foci of infection);
- many species of helminths, entering the digestive tract, release antienzymes, which saves them from death; the digestive process is disturbed, toxic-allergic reactions of various severity appear: urticaria, bronchial asthma, atopic dermatitis;
- stages of development (egg, larva, change of owner);
- the ability of eggs to survive for years in the external environment;
- sexual reproduction, in which the exchange of genetic information takes place, and this is already the highest stage of development, which leads to an increase in the heterogeneous population, ie parasites become less sensitive;
- lack of immunization methods, because the immune response is weak and unstable;
- widespread helminths, many habitats (water, soil, air, plants and animals).
Prevention of parasites in the body
Preventive measures to prevent parasite infestation should be comprehensive. First of all, it is necessary to follow the basic rules of personal hygiene, eat only washed fruits, vegetables, as well as heat-treated fish and meat, drink only clean water.
Most experts advocate the prevention of helminthiasis drugs using pharmaceutical antiparasitic drugs - a parasitologist will help you choose the right drug and correctly calculate its dose.
You can supplement this therapy with folk remedies that have anthelmintic action - for example, eat more onions, garlic, various spices, eat pumpkin seeds regularly.